The Solar Energetic Particle Ionic Charge Analyzer (SEPICA) and the Data Processing Unit (S3DPU) for SWICS, SWIMS and SEPICA
This paper is available in two formats:
HTML
PDF
E. Möbius1, D. Hovestadt2, B. Klecker2, L.M. Kistler1, M.A. Popecki1, K.N. Crocker1, F. Gliem3, M. Granoff1,S. Turco1, A. Anderson1, H. Arbinger2, S. Battell5, J. Cravens6, P. Demain1,J. Distelbrink1, I. Dors1, P. Dunphy1, S. Ellis1, J. Gaidos1, J. Googins1,A. Harasim4, R. Hayes1, G. Humphrey1, H. Kästle1, 2, E. Künneth2,J. Lavasseur1, E.J. Lund1, R. Miller1, G. Murphy7, E. Pfeffermann2, K.-U. Reiche3, E. Sartori1, J. Schimpfle4, E. Seidenschwang2, M. Shappirio1, K. Stöckner3,S.C. Taylor1, P. Vachon1, M. Vosbury1, W. Wiewesiek3, V. Ye1
Abstract
The Solar Energetic Particle Ionic Charge Analyzer(SEPICA) is the main instrument on the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) to determine the ionic charge states of solar and interplanetary energetic particles in the energy range from 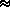 0.2 MeV/nucleon to
0.2 MeV/nucleon to 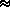 5MeV/charge. The charge state of energetic ions contains key information to unravel source temperatures, acceleration, fractionation and transportprocesses for these particle populations. SEPICA will have the ability toresolve individual charge states and have a substantially larger geometric factor than its predecessor ULEZEQ on ISEE-1 and -3, on which SEPICA is based. To achieve these two requirements at the same time, SEPICA is composed of one high charge resolution sensor section and two low charge resolution, but large geometric factor sections. The charge resolution is achieved by focusing of the incoming ions through a multi-slit mechanical collimator, deflection in an electrostatic analyzer with a voltage up to 30 kV, and measurement of the impact position in the detector system. To determine the nuclear charge (element) and energy of the incoming ions the combination of thin-window flow-through proportional counters with isobutane as counter gas and ion implanted solid state detectors provide for 3 independent
5MeV/charge. The charge state of energetic ions contains key information to unravel source temperatures, acceleration, fractionation and transportprocesses for these particle populations. SEPICA will have the ability toresolve individual charge states and have a substantially larger geometric factor than its predecessor ULEZEQ on ISEE-1 and -3, on which SEPICA is based. To achieve these two requirements at the same time, SEPICA is composed of one high charge resolution sensor section and two low charge resolution, but large geometric factor sections. The charge resolution is achieved by focusing of the incoming ions through a multi-slit mechanical collimator, deflection in an electrostatic analyzer with a voltage up to 30 kV, and measurement of the impact position in the detector system. To determine the nuclear charge (element) and energy of the incoming ions the combination of thin-window flow-through proportional counters with isobutane as counter gas and ion implanted solid state detectors provide for 3 independent 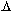 E (energy loss) versus E (residual energy) telescopes. The multi-wire proportional counter simultaneously determines the energy loss
E (energy loss) versus E (residual energy) telescopes. The multi-wire proportional counter simultaneously determines the energy loss 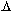 E and the impact position of the ions. Suppression of background from penetrating cosmic radiation is provided by an anti-coincidence system with a CsI scintillator and Si-photodiodes. The data are compressed and formatted in a data processing unit (S3DPU) that also handles the commanding and various automatted functions of the instrument. The S3DPU is shared with the Solar Wind Ion Charge Spectrometer (SWICS) and the Solar Wind Ion Mass Spectrometer (SWIMS) and thus provides the same services for three of the ACE instruments. It has evolved out of a long family of data processing units for particle spectrometers.
E and the impact position of the ions. Suppression of background from penetrating cosmic radiation is provided by an anti-coincidence system with a CsI scintillator and Si-photodiodes. The data are compressed and formatted in a data processing unit (S3DPU) that also handles the commanding and various automatted functions of the instrument. The S3DPU is shared with the Solar Wind Ion Charge Spectrometer (SWICS) and the Solar Wind Ion Mass Spectrometer (SWIMS) and thus provides the same services for three of the ACE instruments. It has evolved out of a long family of data processing units for particle spectrometers.
_______________________
1Institute for the Study of Earth, Oceans and Space, University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH 03824
2Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Postfach 1603, D-85740 Garching, Germany
31. Institut für Datenverarbeitung, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Postfach 3229, D-38106 Braunschweig, Germany
4Fachbereich Elektrotechnik, Fachhochschule Landshut, Am Lurzenhof 4, D-84036 Landshut, Germany
5Battel Engineering, 10020 North 58th Street, Scottsdale, AZ 85253
6Cravens Engineering, 1309 Bristol Drive, Iowa City, IA 52240
7Design Net Engineering, 1968 Mountain Maple Ave., Highlands Ranch, CO 80126
This paper is available in two formats:
HTML
PDF
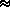 0.2 MeV/nucleon to
0.2 MeV/nucleon to 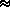 5MeV/charge. The charge state of energetic ions contains key information to unravel source temperatures, acceleration, fractionation and transportprocesses for these particle populations. SEPICA will have the ability toresolve individual charge states and have a substantially larger geometric factor than its predecessor ULEZEQ on ISEE-1 and -3, on which SEPICA is based. To achieve these two requirements at the same time, SEPICA is composed of one high charge resolution sensor section and two low charge resolution, but large geometric factor sections. The charge resolution is achieved by focusing of the incoming ions through a multi-slit mechanical collimator, deflection in an electrostatic analyzer with a voltage up to 30 kV, and measurement of the impact position in the detector system. To determine the nuclear charge (element) and energy of the incoming ions the combination of thin-window flow-through proportional counters with isobutane as counter gas and ion implanted solid state detectors provide for 3 independent
5MeV/charge. The charge state of energetic ions contains key information to unravel source temperatures, acceleration, fractionation and transportprocesses for these particle populations. SEPICA will have the ability toresolve individual charge states and have a substantially larger geometric factor than its predecessor ULEZEQ on ISEE-1 and -3, on which SEPICA is based. To achieve these two requirements at the same time, SEPICA is composed of one high charge resolution sensor section and two low charge resolution, but large geometric factor sections. The charge resolution is achieved by focusing of the incoming ions through a multi-slit mechanical collimator, deflection in an electrostatic analyzer with a voltage up to 30 kV, and measurement of the impact position in the detector system. To determine the nuclear charge (element) and energy of the incoming ions the combination of thin-window flow-through proportional counters with isobutane as counter gas and ion implanted solid state detectors provide for 3 independent 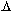 E (energy loss) versus E (residual energy) telescopes. The multi-wire proportional counter simultaneously determines the energy loss
E (energy loss) versus E (residual energy) telescopes. The multi-wire proportional counter simultaneously determines the energy loss 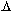 E and the impact position of the ions. Suppression of background from penetrating cosmic radiation is provided by an anti-coincidence system with a CsI scintillator and Si-photodiodes. The data are compressed and formatted in a data processing unit (S3DPU) that also handles the commanding and various automatted functions of the instrument. The S3DPU is shared with the Solar Wind Ion Charge Spectrometer (SWICS) and the Solar Wind Ion Mass Spectrometer (SWIMS) and thus provides the same services for three of the ACE instruments. It has evolved out of a long family of data processing units for particle spectrometers.
E and the impact position of the ions. Suppression of background from penetrating cosmic radiation is provided by an anti-coincidence system with a CsI scintillator and Si-photodiodes. The data are compressed and formatted in a data processing unit (S3DPU) that also handles the commanding and various automatted functions of the instrument. The S3DPU is shared with the Solar Wind Ion Charge Spectrometer (SWICS) and the Solar Wind Ion Mass Spectrometer (SWIMS) and thus provides the same services for three of the ACE instruments. It has evolved out of a long family of data processing units for particle spectrometers.