XI. Relativity
1. Special Relativity
a) Principles of Relativity
i) "the laws of physics the same to all non-accelerating
observers"
no matter how fast they are moving w.r.t.
each other
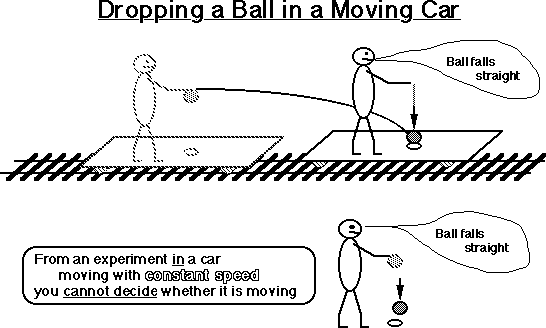

ii) Speed of light = c
the same for everyone

To get velocity:we need to measure
distance and time
b) Einstein's resolution of the dilemma
- Time not absolute (passing slower at
high speed)
- Traveling twin paradox (traveler stays
younger)
- Simultaneity not absolute
- Lengths get contracted at high speed
- Spacetime: observers can agree on combinations
of space & time
c) E = Mc2 or why moving things gain
mass
- Mass can be transformed into energy -->
energy source of the stars
- Then:
- Energy can also be mass -->
M = E/c2
- Mass into motion --> Kinetic Energy
"Kinetic Mass"
- m -->
¥ as velocity --> c
- Can't ever get to c!!!!
- Energy goes into increasing mass rather
than increasing speed
2. General Relativity:
A) Basic principles
- Response to gravity is independent
of object... or in other words
- acceleration is equivalent to gravity
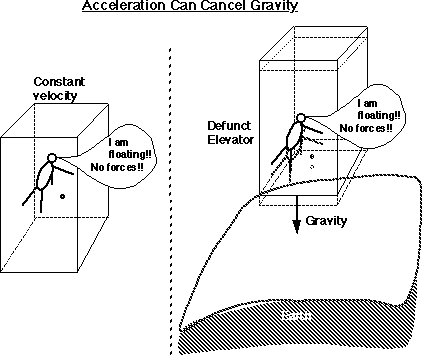
- based on "Inertial Mass = Gravity
Mass" mi = mg
B) Effects of Gravity on Time
a) Gravitational redshift
- in accelerated spaceship: detector faster
while light is on the way
- Doppler red shift of light
- in gravity:light looses energy
- Gravity red shift(tests: white
dwarfs, precise experiment in lab)
b) Gravitational twin paradox
- time runs slow near huge mass
(test: atomic clocks flown at different
elevations)
C) Curvature of space
- Light is bent in gravity fields:
- Know: light is taking a straight
path?
- Better:light is taking shortest path!!This
can be curved!
- Analogy: on Earth we always take
the great circle route as the shortest
- (transatlantic routes of jet liners)
- Mass (and energy) produce a curved
space-time
D) Tests of general relativity
a) Gravitational deflection of light
- 1919: First test of Einstein's prediction
of gravitational deflection of light
During total solar eclipse

b) Spacetime curvature produces non-Keplerian
motion
- Analogy: ball rolling on a dented tabletop
- The orientation of the orbit of Mercury
turns around (like a rosetta)
- not a perfect ellipse ("perihelion
shift")
c) Gravitational waves:propagating
ripples in spacetime
- Observation: Pulsar (a very precise clock!)
orbiting neutron star slowing down
due to gravity wave emission (energy loss)
- When will they be directly observed?
E). Black Holes
- A hole in spacetime everything falls
"out of our spacetime"
- Analogy: A hole in a tabletop everything
falls through
a) Principles
- if M > 3(?) Msun, collapse continues
- Gravity increases and even light can't
escape
b) Possible example:
- Cygnus X-1: A special binary X-ray source
- 30 Msun normal star moves
- Compact X-ray companion must have >
6 Msun
- evidence
that the compact object is a black hole
c) Features of a Black Hole
- Concentrates mass inside the "Schwarzschild
radius" = "event horizon"
- (Not difficult for supermassive black
holes > 108 solar masses)
- Sun would have to be squeezed to a radius
of 3 km!!
- Can only grow: Black Holes dig their
own holes in spacetime
- Nothing will ever come back!
- Can only have mass, angular momentum,
electric charge
- No structures"Black holes have no hair"

Chapter 12




