PHYSICS 406 - Introduction to Modern Astronomy
March 8, 1996
SECOND EXAM
Note: Each Question counts 2 points. 80 points correspond
to 100 on the grade scale in the Syllabus.
Where you find the remark: (More than one answer), providing all
correct answers leads to full credit. Only one correct
answer leads to 1 point. Incorrect additional answer leads
to subtraction of the first point.
1. During waning half moon you have built a sand castle on the
beach a couple meters away from the water line at high tide. If
nobody will destroy it deliberately and no rain falls, what will
happen to it?
- It will remain there, since the tides at half moon are the highest.
- It will be destroyed sometime during the next week when the tides grow
towards new moon.
- It will be destroyed during the night, since the opposite tidal bulge is
much higher.
- It will be destroyed only about three weeks later, since the tides are
the highest around full moon.
2. The tidal bulge on the side of the Earth opposite to the moon is created
- by the centrifugal force due to the rotation of the Earth
- because the Earth has to remain balanced
- by the centrifugal force due to the rotation of the Earth about the common
gravity center of Earth and moon
- by the gravitational pull of the sun
3. The moon is gradually moving further away from Earth. What is the reason?
- The gravitation of Earth is gradually decreasing with time.
- The Earth loses angular momentum because it is slowed down by tidal effects.
Therefore, the moon must gain angular momentum and move further away.
- The sun plays a role in the tides and pulls the moon gradually further
away from Earth.
- The moon is pushed further away from Earth by the solar wind.
4. A satellite is at a distance of 10 earth radii from the center of Earth.
How strong is the gravitational force that pulls at the satellite?
- 10 times less than on the Earth's surface, since it is 10 times farther
away from the Earth's center than an object on the surface and the force goes
down with the distance from the center
- 100 times less than on the Earth's surface, since it is 10 times farther
away from the Earth's center than an object on the surface and the force goes
down with the square of the distance.
- No gravitational force pulls at the satellite, since it does not fall back
to Earth.
- 9 times less than on Earth, since it is 9 earth radii above the surface
and the force goes down with the distance from the surface
5. When a planet is closer to the sun its speed is higher than when it is farther
away. In this case, the Angular Momentum is
- larger than when far away
- smaller than when far away
- the same as when far away
- The answer depends on the size of the planet.
6. How would you derive the mass of a galaxy?
- From the angular size of the galaxy in the sky
- From the number of stars in the galaxy
- From the velocity and the distance of the stars in the galaxy about their
common center
- From the brightness of the galaxy
7. Radio telescopes are much larger than optical telescopes. What is the main
reason?
- They have to be large to compete with the radio stations on Earth.
- Because the wavelength of radio waves is much longer than that of visible
light, the radio dishes have to be larger to allow a good angular resolution.
- Radio signals from celestial objects are much weaker than their emission
in the visible wavelength regime. Thus the dishes have to be larger.
- Radio signals are strongly blocked by the Earth's atmosphere. Thus a large
dish is needed to receive the signals.
8. Volcanism needs an energy source to melt the material which is expelled
by volcanoes and to drive the material out. Name energy sources for volcanism
in the solar system (2 energy sources for full credit, 3 extra credit!). Short
answer ___________________________________________________________________
9. From which observations can we deduce that the Earth's core is partially
liquid? (More than one answer)
- A hole has been drilled to the center of Earth and liquid core material
has been retrieved.
- From seismic probing of the Earth's interior. Only the seismic P waves
make it through liquids.
- From the existence of the Earth's magnetic field.
- We get crude oil from as deep as the center of Earth.
10. Jupiter has a "Van Allen" radiation belt. What can you conclude?
- Jupiter has a very hot atmosphere.
- Jupiter has magnetism and a magnetosphere.
- Jupiter has no atmosphere so that it can radiate freely into space.
- The folks on Jupiter have nuclear power plants.
11. On the moon many big craters are found with additional small craters on
the crater walls and inside. What was the sequence of events to create these
structures?
- The big craters were formed after the small craters.
- These groups of craters were formed simultaneously.
- The small craters were formed after the big ones.
- No clue is possible from this observation.
12. The size of meteoritic impact craters on the moon mainly depends on
- the shape of the meteorite;
- the kind of material in the meteorite;
- the size of the meteorite
- the kinetic energy of the meteorite;
- the kind of material on the moon's surface.
13. What are the Van Allen Radiation Belts?
- the dump for radioactive waste of our civilization
- a region with energetic charged particles trapped in the Earth's magnetic
field
- the region with the most intense UV radiation on Earth
- the region where we can observe X-rays on Earth
14. For this question on magnetic reconnection refer to the following figure
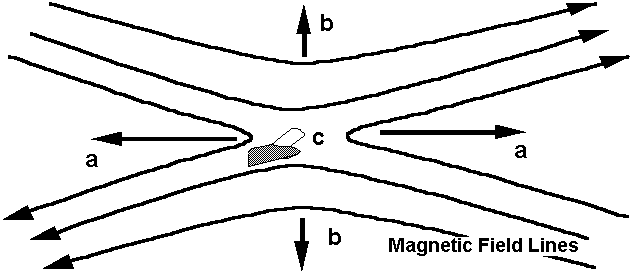
Opposite magnetic field lines that come close to each other want to reconnect
as shown in the figure. In the Earth's magnetosphere magnetic fields are immersed
in plasma. In which direction will the plasma be forced to flow? (Refer to the
letters in the figure.)
- because it clings to the field lines and goes where they stretch
- because it is reflected by the magnetic mirror
- because it gets squeezed out of the field like out of a toothpaste tube
- the plasma won't go anywhere, it is not bothered by the field
15. What is a gas called which contains free electrons and ions? Short answer
__________________
16. The aurora is caused by
- sunlight reflected off the Earth's upper atmosphere.
- a TV program from outer space.
- high-energy electrons from the magnetosphere hitting the Earth's upper
atmosphere.
- lightning in the night sky.
17. The Earth's "geomagnetic tail" is produced by
- the centrifugal force due to the Earth orbiting about the sun.
- the Earth's rotation.
- the moon's gravity.
- the solar wind.
18. In addition to Earth name at least 3 more planets in the solar system
with magnetic fields. (more than 3 -> extra credit) Short answer _______________________________________________________________
19. What made the long journey of Voyager to almost all of the outer planets
possible with a moderate use of fuel?
- the use of a compact nuclear power plant to produce the thruster energy
- the use of the solar wind by means of a solar wind sailing technique
- the use of planetary magnetic fields to accelerate Voyager
- the use of the planets' gravitational fields during the flyby of Voyager
20. Which of the following planets is at the greatest distance from the Sun?
- Uranus
- Earth
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Mercury
21. The surface of Venus is hotter than the surface of Mercury. Why?
- Venus is closer to the Sun.
- Venus' atmosphere contains a lot of carbon dioxide, creating a strong greenhouse
effect.
- The atmospheric pressure at Venus' surface is very large.
- Venus has an extremely hot core.
22. Which are the slowest moving photons?
- Radio wave photons
- Gamma ray photons.
- All electromagnetic radiation moves at c, the speed of light.
- Particles in the solar wind.
23. What is the reason for the drift of the continents?
- The continental drift is an effect of the tides.
- The Earth's magnetism drives the continents.
- The continents are floating on the ocean water and driven by winds.
- The continents are floating on the hot mantle material and are driven by
convection.
24. A Geiger counter can be used to detect (more than 1 possible)
- visible light.
- X-ray radiation.
- radio waves
- energetic ions
- seismic waves
25. A star that appears red
- is hotter than the sun
- reflects only the red part of the light spectrum
- is cooler than the sun
- consists mostly of rusty iron
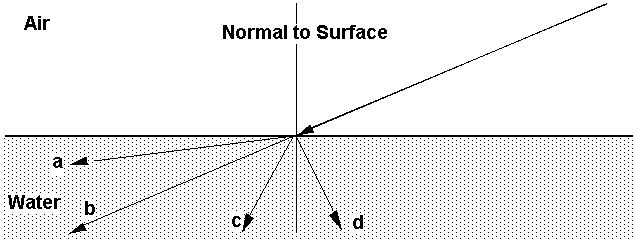
26. For a light ray entering water refer to the following schematics. Which
of the light paths is the correct one?
27. The maximum diameter of your pupil is Å 6 mm, its focal length Å
3 cm. There is a star which you can see with the naked eye just barely. You
want to also observe a companion of this star which is 100 times fainter. What
do you do to achieve this? (Use only the necessary minimum, because otherwise
it gets too expensive!)
- You buy a telescope with a focal length of 3 m.
- You buy a telescope with a diameter of the objective of 60 cm.
- You buy a telescope with a focal length of 30 cm.
- You buy a telescope with a diameter of the objective of 6 cm.
28. The Enterprise is just passing a star exactly on its right side, while
flying at (half impulse) half the speed of light. Where does stellar cartography
have to point the telescope to see the star?
- Exactly at right angle to the right because that is where the star is located.
- To the right and slightly backwards because at the time the light arrives
at the Enterprise the star is already behind it.
- To the right into the forward direction because the light arrives from
the forward direction due to the motion of the Enterprise.
- To the left because directions are swapped when one is moving.
29. Which electromagnetic radiation of the examples given below has the shortest
wavelength?
- radio
- x-rays
- infrared
- yellow light
- ultraviolet
30. Name several types of electromagnetic radiation from celestial objects
that do not reach the Earth's surface. (3 for full credit, 4 extra credit) Short
answer:_________________________________________________________________
31. Give two reasons why Hubble space telescope was built? Short answer _________________
Short answer _________________
32. Why did Newton use mirrors instead of lenses for the objectives of his
telescopes?
- He was left handed and preferred the mirror image.
- Mirrors avoid the problem of chromatic aberration.
- Mirrors were easier to fabricate than lenses during Newton's time.
- Mirrors collect light better than lenses.
33. How can a mirror be used to create an image in an X-ray telescope?
- In the same way as in optical telescopes.
- X-rays must bounce off the mirror at a very flat angle.
- Instead of using a concave mirror a convex mirror is used.
- Mirrors cannot be used in X-ray telescopes at all.
34. The "Milky Way" looks to our unaided eyes like a "band of
light" across the sky. Through a telescope it is seen to consist of millions
of stars. Why?
- The telescope has better resolving power than our eyes.
- Our eyes have better resolving power than the telescope.
- Our eyes are more sensitive to the effects of atmospheric turbulence.
35. The giant planets have densities much lower than the inner planets. What
is the reason?
- The sun's gravity is lower out there. Therefore, their density is decreased.
- The giant planets mainly consist of the light elements H and He.
- The gravitational force of these planets is lower than that on the inner
planets. Therefore, they are not so compact.
- The centrifugal force on their orbit is larger and balances the gravity.
36. Not all of the planets and moons in the solar system have an atmosphere
of gas around them. Which of the following conditions (more than one) will favor
the loss of an atmosphere into space?
- A bright and shiny surface of the planet/moon will reflect the gas atoms
and molecules and thus send them off into space.
- A hot temperature on the planet/moon will make the atoms and molecules
move fast that they can escape from it.
- A fast rotation of the planet/moon will send the atmosphere off into space
by the centrifugal force
- A strong solar wind will blow the atmosphere away from the planet/moon.
- A weak gravitation of a small planet/moon with a small mass cannot hold
an atmosphere around the object.
- A planet without a magnetic field will lose its atmosphere.
37. The greenhouse effect heats a planet because
- more sunlight strikes the planet's surface than normal.
- the surface of the planet is darker than normal.
- infrared radiation is trapped by the planet's atmosphere.
- cloud cover prevents the atmosphere from escaping.
- internal heat sources of the planet that contribute to heating.
38. What is a consequence of the precession of the Earth?
- the magnetism of the Earth
- Polaris will not be at the North Celestial Pole forever
- the slowing down of the Earth's rotation
- the seasons
39. Recently the detection of several planets orbiting about other stars that
are similar to our sun has been reported. How were these planets found?
- The crew of the Enterprise found these planets on their most recent voyage.
- The Hubble space telescope has taken photographs of these planets.
- The motion of the center stars in response to the gravitational pull of
the orbiting planets was discovered and the existence of the planets was deduced.
- Radio telescopes have found radio transmissions from intelligent beings
on these planets.
40. What makes the diameter of Saturn at the equator larger than that from
pole to pole?
- Saturn is squeezed flat because it consists mainly of gases.
- The solar wind blows Saturn flatter at the poles.
- The tidal forces of its moons extend Saturn at the equator.
- The centrifugal force due to Saturn's fast rotation extends the diameter
at the equator.
- Saturn's rings make the equatorial diameter larger.
Bonus Question. When Ole Römer observed Io orbiting Jupiter he wanted
to use it as a huge clock for navigation. He observed the time of passage of
Io in front of Jupiter, i.e. he set the clock, during opposition. What did he
observe during conjunction of Jupiter with the sun?
- Io passed Jupiter earlier than he expected during conjunction, i.e. the
clock went ahead.
- The times of passage were the same as predicted, i.e. Io could be used
as a good clock.
- Io passed Jupiter later than he expected during conjunction, i.e. the clock
lagged behind.